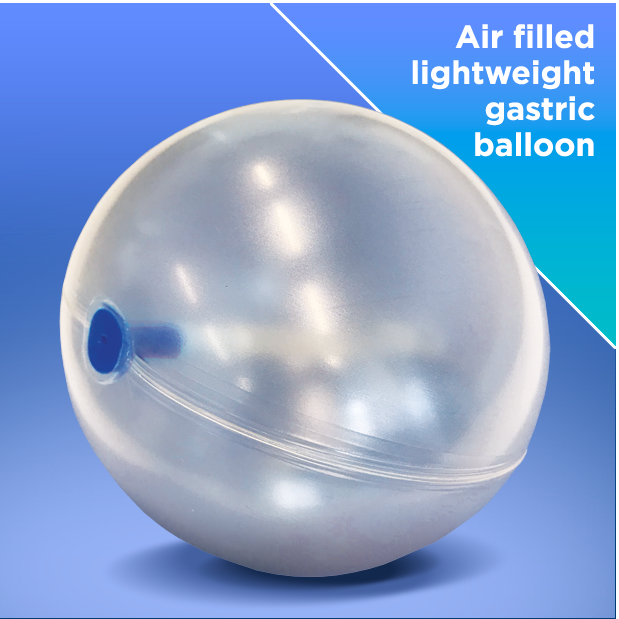

Heliosphere
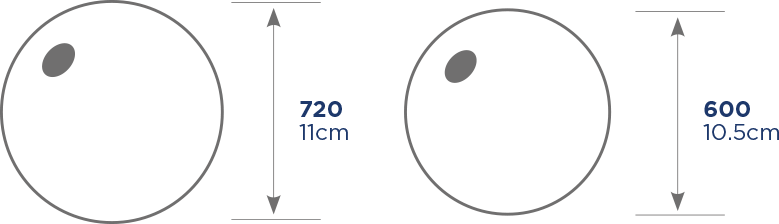
600/720
The new gastric balloon technology
More comfortable, with less side effects and class leading weight loss up 24kg 1.Heliosphere® is Next Generation gastric balloon technology. Filled with air, the ultra-lightweight allows free natural movement in the stomach so no sustained pressure on gastric mucosa reducing the risk of complications and making it more comfortable for the patient.
The widest range of patients
Certified ≥ 27 BMI and with two sizes available, 600cc and 720cc, you can provide the best individual treatment for the widest range of patients.
A less complex insertion procedure
The light sedation insertion technique via normal endoscopic procedure with no complicated and cumbersome saline injection required.
Inflated with air
Ultra-light weight (< 10 g) means less chance of nausea and vomiting and better patient tolerance.
Implantation duration
6 months.
Comfortable robust and safe
Double wall design gives reliable treatment duration and polyurethane construction means no silicone blockage risk.
Simple Insertion
- Low sedation.
- Normal endoscopic procedure.
- No saline solution required.
Simple Extraction
- Normal endoscopic procedure.
- No requirement for saline suction.
- Polyurethane material means once perforated the balloon naturally returns to cylindrical shape with reduced requirement for suction.
- Unlike water filled silicone balloons the Heliosphere® will deflate completely without trapping any pockets of air.
Information
Gastroplasty surgery to treat obesity is considered only after medically managed diets have failed to achieve long-term weight loss. It is important for the success of treatment that the use of the HELIOSPHERE® 600/720 intragastric balloons is accompanied by medical and dietetic monitoring.
Conditions
The balloon has broad suitability conditions. From overweight patients (BMI ≥ 27) to obese patients who do not meet the criteria for bariatric surgery, to super-obese (BMI ≥ 50) as a gateway to bariatric surgery.Results
Once inflated, the balloon reduces the nominal volume of the stomach. By acting freely in the stomach, HELIOSPHERE® causes a rapid feeling of satiety at meals. The patient eats less and loses weight.
Efficiency
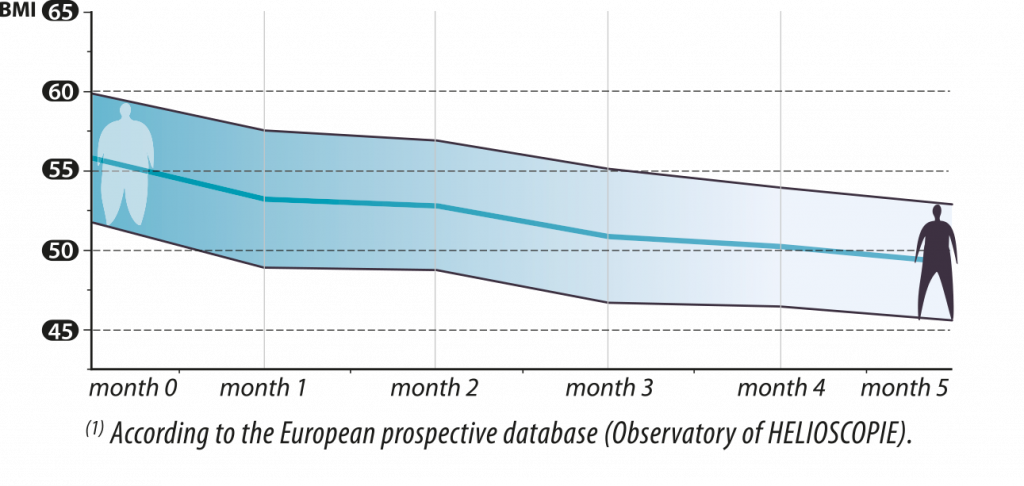
Loss of weight up to as much as 24KG.1
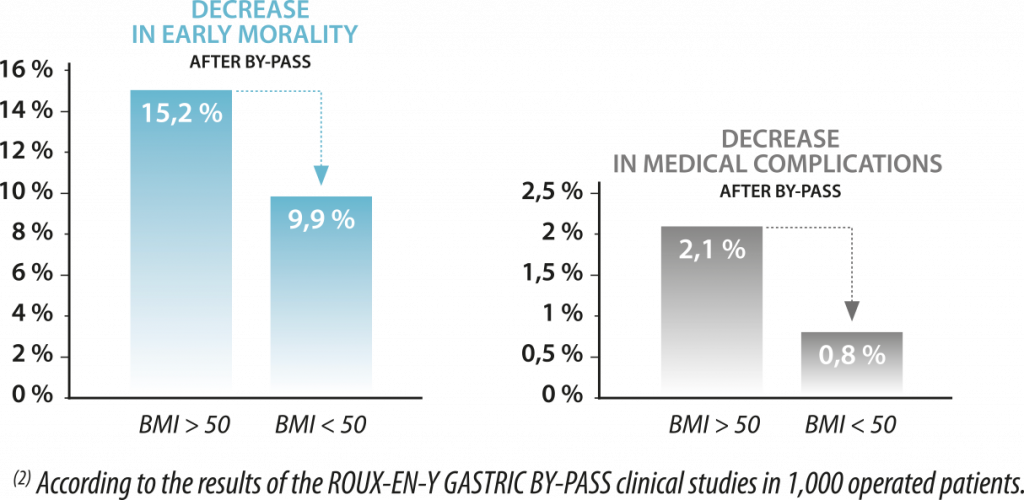
Lowering of surgical risks thanks to the pre-operative reduction in weight. (Flancbaum observes a direct link between surgical risks and the initial Body Mass Index of patient. The reduction in the BMI before by-pass lowers the risk of medical complications or early mortality.3)
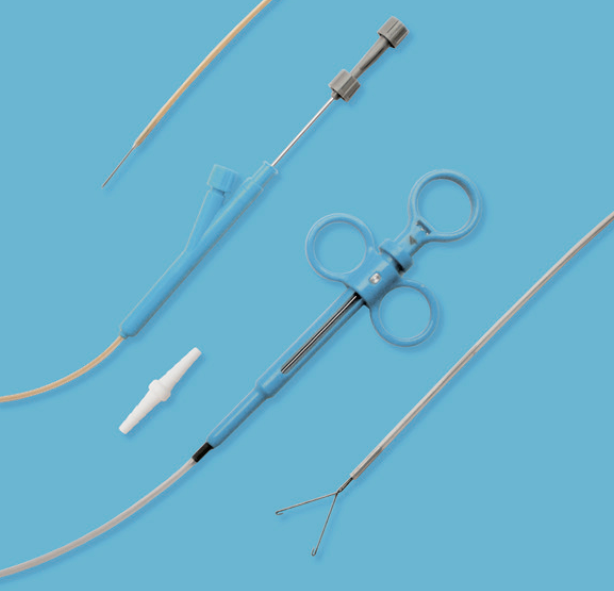
1 deflation needle
1 pair of extraction forceps
1 universal connector
Reduction of BMI in 46 patients1
Correlation of surgical risks with initial BMI patients2
Bibliography
1 Erdem, H., et al. (2016). “Effects of Intragastric Balloon on Body Mass Index, Lipid Profile and Blood Glucose Regulation: A Prospective Study.” Dicle Tıp Dergisi 43(1).
1 Palmisano, S., et al. (2016). “Intragastric Balloon Device: Weight Loss and Satisfaction Degree.” Obesity surgery 26(9): 2131-2137.
1 Espinet Coll, E., et al. (2017). “Multicenter study on the safety of bariatric endoscopy.” Rev Esp Enferm Dig 109(5): 350-357.
2 According to the European prospective database (Observatory of HELIOSCOPIE).
3 Factors Affecting Morbidity and Mortality of Roux-en Y Gastric Bypass for Clinically Severe Obesity: An Analysis of 1,000 Consecutive Open Cases by a Single Surgeon. Louis Flancbaum. J Gastrointest Surg (2007) 11:500-507.
Tolerance And Efficacy of an Air-filled Balloon In Non-Morbidly Obese Patients… F. Mion. Obesity Surgery, 2007; 17, 764-769.
Posters from the World Congress of IFSO: Air-Filled Intragastric Balloon (Bag): Italian Multicentric Results. A. Giovanelli (2007).
Heliosphere intragastric Air Balloon: Our Initial Experience in the Dominican Republic. Dk Ramirez. (2006), Intragastric Balloon for Obesity: Comparative Study With 420 Patients: New Generation Air-filled vs Liquid-Filled. C. Hermida. (2006) or from the UEGW: Primary Experience With Air-Filled Intragastric Balloon Compared With Intragastric Balloon Literature Data. H. Claudez (2005) ‘.
